Melanoma – Its Prevention, Symptoms, and Treatments
Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, is the most serious form of skin cancer. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays is believed to be one of the major causes of it. This cancer occurs in the melanocytes, the cells that produce the pigment melanin that gives the skin its color.
Only 1% of all skin cancers can be melanoma. Since it is a serious type of cancer, it is important to know the symptoms to ensure early detection and treatment. Melanoma is commonly seen on the back, face, arms, and legs. It can also occur on the soles or palms.
1. Symptoms of melanoma
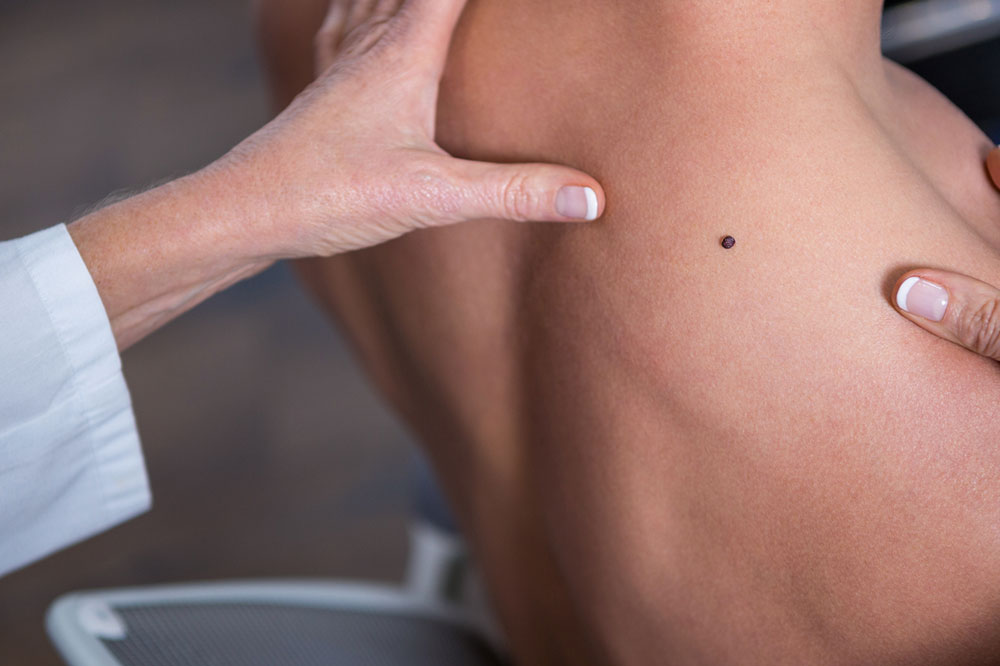
Some early signs of melanoma include changes in a mole that is already present on the body. It also includes new growths of the skins, which can be moles or other types of growth. The term ABCDE can be used to diagnose if a mole is a melanoma:
- A stands for asymmetric shape, indicating a mole that is irregular in shape.
- B is for an irregular border of the mole that can be notched or scalloped.
- C stands for change in the color of the mole or the mole having an uneven distribution of color.
- D is the diameter of the mole (more than 6 millimeters large).
- E stands for evolving, which happens when the mole is changing in size, shape, or color.
Some other symptoms of melanoma include:
- A sore that does not heal well
- A sore or spot that begins to bleed
- Itching, pain, or tenderness in a sore or spot on the skin
- A pale or waxy appearance of a sore or spot
- A lump or spot that looks ulcerated in appearance
- A spot that is red, rough, or scaly while being flat
If any of these are observed, it would be better to let a skin specialist evaluate the mole, sore, spot, or lump.
2. Treatment
The treatment for melanoma includes:
- Surgery to remove the melanoma
- Surgery to remove the lymph nodes if cancer has spread
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
- Immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer after surgery
3. Prevention
It is possible to try and prevent melanoma by taking the following measures:
- Avoiding sunburn or direct exposure to the sun, especially at noon
- Protecting exposed skin through clothes, hat, and by using sunscreen (with an SPF factor of at least 30)
- Standing under the shade on a sunny day. This is especially needed for children
- Avoiding the use of tanning booths and sunbeds
- Vitamin D supplements can be taken so that exposure to sunlight can be avoided